Syzkaller Note
Published:
Syzkaller
Syzkaller is the most famous kernel fuzzer in this world. It’s developed by Google and is open-source. It has been widely adopted by the kernel community to detect bugs in kernel source code.
How it works
Before using it, I’d like to dig out what components consists Syzkaller and how they work. According to the official documentations, this figure can demonstrate the workflow of Syzkaller.
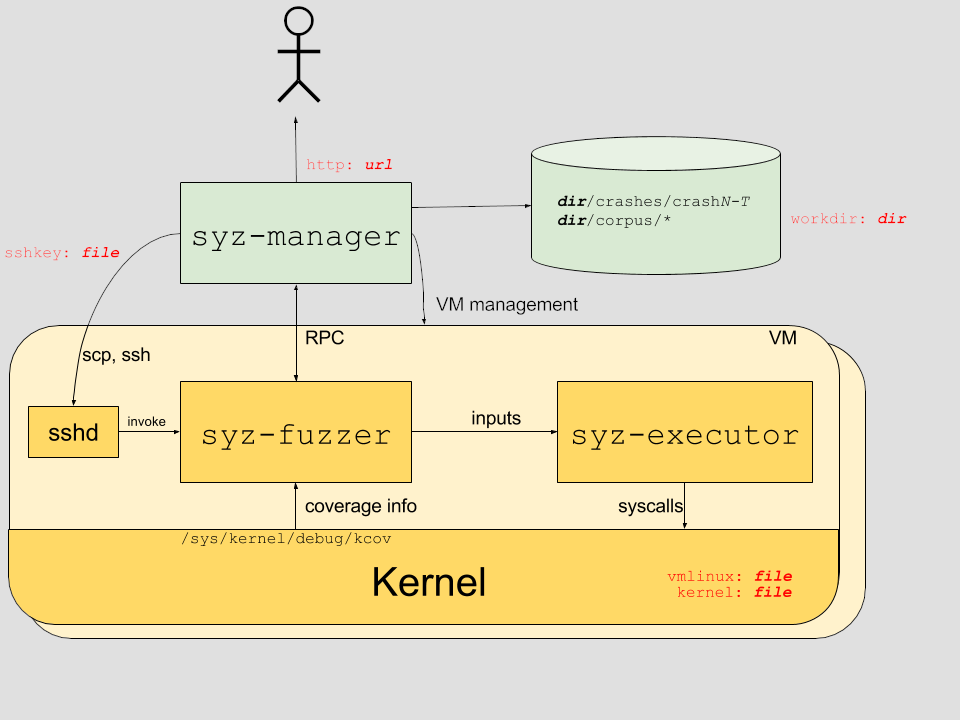
In a simplified overview, Syzkaller has a “manager” to control the test system. It employs multiple virtual machines with fuzzers inside them. The fuzzers will generate and run small programs which invoke a sequence of syscalls. Then the executors will use the randomized values as input data and execute these small programs. At mean time, fuzzer will use coverage info provided by KCOV to guide the fuzzing.
Setup
Before building Syzkaller, you need the following toolchains installed:
- Golang(1.22+)
- C compiler with coverage support()
Let’s first install Golang, it’s quite easy, just run the following commands:
wget https://dl.google.com/go/go1.22.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xf go1.22.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
export GOROOT=`pwd`/go
export PATH=$GOROOT/bin:$PATH
Then, let’s obtain the source code of Syzkaller and build it locally.
git clone https://github.com/google/syzkaller.git
cd syzkaller
make
Note that if you want to do a cross-OS/arch testing, you may need to specify some arguments in make. For example, TARGETOS and TARGETARCH.
The next step is to build the linux kernel:
git clone https://github.com/trovalds/linux.git
cd linux
make defconfig
To improve the performance of Syzkaller, you need to manually change some configurations in the kernel config. See Linux kernel configs
Here I just add basic KCOV support and some other chore configurations:
CONFIG_KCOV=y
CONFIG_KCOV_INSTRUMENT_ALL=y
CONFIG_KCOV_ENABLE_COMPARISONS=y
CONFIG_DEBUG_FS=y
CONFIG_DEBUG_INFO_DWARF_TOOLCHAIN_DEFAULT=y
CONFIG_KALLSYMS=y
CONFIG_KALLSYMS_ALL=y
CONFIG_NAMESPACES=y
CONFIG_UTS_NS=y
CONFIG_IPC_NS=y
CONFIG_PID_NS=y
CONFIG_NET_NS=y
CONFIG_CGROUP_PIDS=y
CONFIG_MEMCG=y
CONFIG_CMDLINE_BOOL=y
CONFIG_CMDLINE="net.ifnames=0"
append these configurations to .config and then do make olddefconfig.
make olddefconfigmeans generating a default config and override some of the values using the old config
Now we can build the kernel:
make -j`nproc`
Syzkaller executes programs in VM, so we also need QEMU. To install it, just type:
sudo apt install qemu-system-x86-64
After installation, use the create-image.sh script to create a Debian image.
mkdir image
cp syzkaller/tools/create-image.sh image
cd image
# for those who in Mainland China, you may need to use the mirrorsite
sed -i -e 's~sudo debootstrap .*~\0 https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/debian/~' create-image.sh
./create-image.sh
This script will generate three files in image directory:
bullseye.imgvirtual machine imagebullseye.id_rsaprivate ssh keybullseye.id_rsa.pubpublic ssh key
Now start qemu and test if it works well, use the script below:
#!/bin/bash
KERNEL="$(pwd)/linux"
IMAGE="$(pwd)/image"
qemu-system-x86_64 \
-m 2G \
-smp 2 \
-kernel "$KERNEL"/arch/x86/boot/bzImage \
-append "console=ttyS0 root=/dev/sda earlyprintk=serial net.ifnames=0" \
-drive file="$IMAGE"/bullseye.img,format=raw \
-net user,host=10.0.2.10,hostfwd=tcp:127.0.0.1:10021-:22 \
-net nic,model=e1000 \
-enable-kvm \
-nographic \
-pidfile vm.pid \
2>&1 | tee vm.log
if qemu starts successfully, you can login as root without password. Also, you need to open another terminal and test ssh. Use command ssh -i bullseys.id_rsa -p 10021 -o "StrictHostKeyChecking no" root@localhost to connect to VM, if it connects successfully, then congraulates, you have setup all you need.
Now we are all done! Let’s just start fuzzing!
Fuzzing
To start syz-manager, you need a config file for syz-manager, an example is
{
"target": "linux/amd64",
"http": "127.0.0.1:56741",
"workdir": "$GOPATH/src/github.com/google/syzkaller/workdir",
"kernel_obj": "$KERNEL",
"image": "$IMAGE/bullseye.img",
"sshkey": "$IMAGE/bullseye.id_rsa",
"syzkaller": "$GOPATH/src/github.com/google/syzkaller",
"procs": 8,
"type": "qemu",
"vm": {
"count": 4,
"kernel": "$KERNEL/arch/x86/boot/bzImage",
"cpu": 2,
"mem": 2048
}
}
You need to replace the environment varibles accordingly instead of copying and pasting. Save the file as test.cfg, and specify it when start syz-manager:
mkdir workdir # this is what directory you specify in the config
./syzkaller/bin/syz-manager -config=test.cfg
If anything goes well, fuzzing has began. You will see the logs like:
2024/12/04 17:18:30 serving rpc on tcp://43585
2024/12/04 17:18:30 serving http on http://127.0.0.1:56741
2024/12/04 17:18:31 skipped 15 seeds
...
You can also view the dashboard in your browser, just visit http://1237.0.0.1:56741 and you will see the dashboard.
